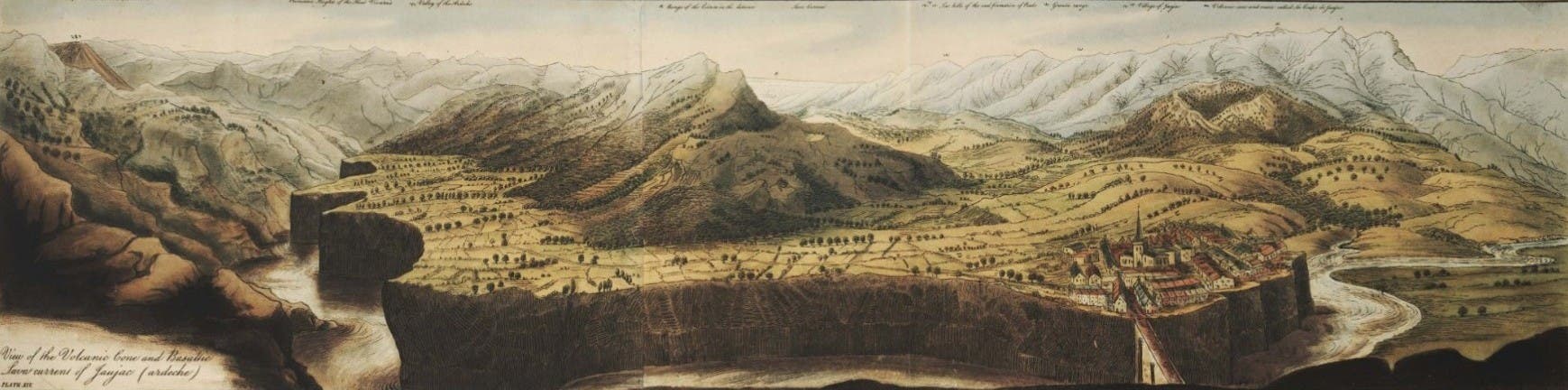
Volcanoes in the Andes, 1751
La Condamine, Charles Marie de (1701-1774). Journal du voyage fait par ordre du roi, a l’équateur. Paris: Imprimerie Royale, 1751.
In 1735 the French Academy of Sciences sent a scientific mission to Ecuador to measure the length of a degree of the meridian along the equator. They spent nine years at their task. One of the mathematicians, La Condamine, took an interest in the mountains of the Andes that flank Quito, their base of operations. In June of 1742, having climbed the peak of Pichincha to examine its crater, La Condamine observed an eruption of a volcano called Cotopaxi. Cotopaxi is the highest active volcano in the world, towering 15,000 feet higher than Mount Vesuvius.
In his 180-degree wide-angle view of the mountains that lie west of Quito, La Condamine shows Cotopaxi at the far left (identified with the number 2), in the process of erupting. Pichincha, the volcanic summit from which he observed Cotopaxi is mountain number 10, the highest peak just to the right of the center.
Laissus, Yves, “La Condamine, Charles-Marie de,” in DSB 15:269-273.